Key Takeaways From Stringent Standards Set by EPA's New Emissions Rule
by Tom Quimby, On-highway Journalist
Published 05-13-24
Submitted by Cummins, Inc.

The Environmental Protection Agency has announced the final rule for Phase 3 of its Greenhouse Gas Emissions for heavy-duty vehicles. Since issuing Phase 1 of its GHG regulations in 2011, EPA emissions rules for all vehicle classes have become increasingly rigorous. The latest Phase 3 rule continues to address heavy-duty vehicles which the EPA separates into five categories: light heavy-duty vocational; medium heavy-duty vocational; heavy heavy-duty vocational; short-haul (day cab) tractors; and long-haul (sleeper cab) tractors.
In its introduction for GHG Phase 3, EPA pointed out that its latest phase sets new carbon dioxide (CO2) emission standards for heavy-duty vehicles through model year 2032 “with more stringent CO2 standards phasing in as early as MY 2027 for certain vehicle categories.” Prior to finalizing GHG standards, EPA considers comments from various stakeholders like manufacturers, fleets, owner-operators, trucking associations, environmental interest groups and private citizens. The standards are technology-neutral and performance-based, allowing each manufacturer to choose what set of emissions control technologies is best suited to meet the standards and the needs of their customers.
“We have assessed and demonstrated that these standards are appropriate and feasible considering cost, lead time, and other relevant factors,” EPA noted in its executive summary.
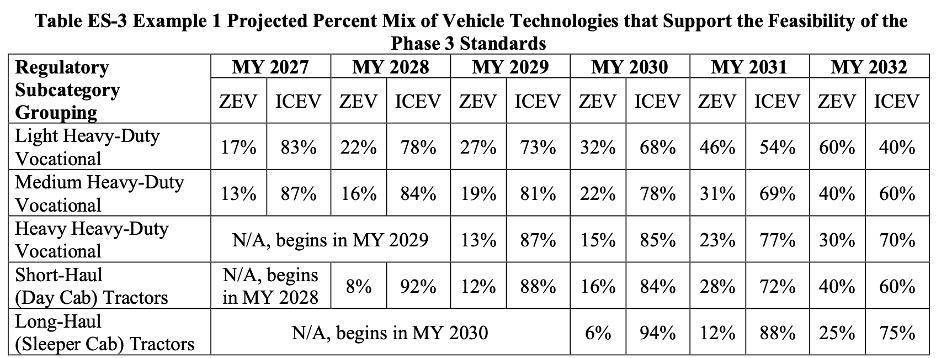
While there is plenty to read in all 392 pages of GHG Phase 3, let’s look at five major takeaways:
- The initial rollout for Phase 3 GHG impacts only MY 2027 light heavy-duty and medium heavy-duty on-highway vocational vehicles such as commercial chassis cabs, panel vans and box trucks (complete pickups not included) ranging from Class 2b to 3, or 8,500 to 14,000 lb. gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR). Though EPA does not endorse any particular technology and does not mandate the use of zero-emission vehicles (ZEVs), they do project a possible path of compliance for MY 2027 light heavy-duty vocational with 17% ZEVs and 83% powered by internal combustion engines (ICE). MY 2027 medium heavy-duty vocational could be a mix of 13% zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) and 87% ICE.
- Lower Phase 3 standards come next for MY 2028 short-haul (day cab) tractors which the EPA anticipates will be a combination of 8% ZEV and 92% ICE. MY 2029 heavy heavy-duty vehicles follow with a projected mix of 13% ZEV and 87% ICE. MY 2030 long-haul (sleeper cab) bring up the rear with an anticipated adoption rate of 6% ZEV and 94% ICE. Check the EPA’s table below for other projected rates of adoption for subsequent model years through 2032.
- EPA set its GHG Phase 3 timeline based on current and projected advances to prevent and control GHG emissions. The EPA makes clear that it does not pick and choose when it comes to emissions reduction. The agency recognizes that fleets and owner-operators will continue to adopt emerging technologies. Options such as all-electric, fuel cell and internal combustion will continue to play a vital role. A range of technologies can meet the demanding heavy-duty power requirements while continuing to reduce emissions along the way. For example, the Biden administration recently acknowledged the importance of emissions reduction through support of research and development of hydrogen internal combustion engines, including Cummins’ X15H. EPA states in GHG Phase 3 that hydrogen engines have essentially a 100% reduction in CO2 emissions.
- The EPA also announced that it is adding warranty requirements for batteries and other components of zero-emission vehicles and requiring customer-facing battery state-of-health monitors for plug-in hybrid and battery electric vehicles.
- EPA notes it has improved its analysis of infrastructure readiness for heavy-duty all-electric, hydrogen fuel cell and hydrogen combustion trucks. Citing growing public and private funding sources, the agency states, “there are significant efforts already underway to develop and expand heavy-duty vehicle electric charging and hydrogen refueling infrastructure.”
Through Cummins’ multi-solutions approach, the company can offer customers the industry’s broadest portfolio of low- and zero-emissions, allowing customers to meet emissions regulations in a way that also best meets their business needs.

Cummins, Inc.
Cummins, Inc.
Cummins Inc., a global power leader, is a corporation of complementary business segments that design, manufacture, distribute and service a broad portfolio of power solutions. The company’s products range from diesel, natural gas, electric and hybrid powertrains and powertrain-related components including filtration, aftertreatment, turbochargers, fuel systems, controls systems, air handling systems, automated transmissions, electric power generation systems, batteries, electrified power systems, hydrogen generation and fuel cell products. Headquartered in Columbus, Indiana (U.S.), since its founding in 1919, Cummins employs approximately 61,600 people committed to powering a more prosperous world through three global corporate responsibility priorities critical to healthy communities: education, environment and equality of opportunity.
More from Cummins, Inc.

