AllianceBernstein: Making Sense of ESG-Labeled Bonds
Published 03-30-22
Submitted by AllianceBernstein
Salima Lamdouar| Portfolio Manager—Sustainable Fixed Income
Tiffanie Wong, CFA| Director—Fixed Income Responsible Investing Portfolio Management; Director—US Investment-Grade Credit
We’re optimistic that securities labeled as environmental, social and governance (ESG) bonds will help create a better, more sustainable world. And investors are just as eager to buy these bonds. But with the recent proliferation of ESG bond structures, the investment landscape has become more complex—and potentially confusing.
Assessing an ESG-labeled bond means delving deeper than an issuer’s financials, into the bond’s governing framework and its fit with the overall sustainability of the issuing company. In other words, to make the right investment choices, investors must understand the different structures and their investment implications.
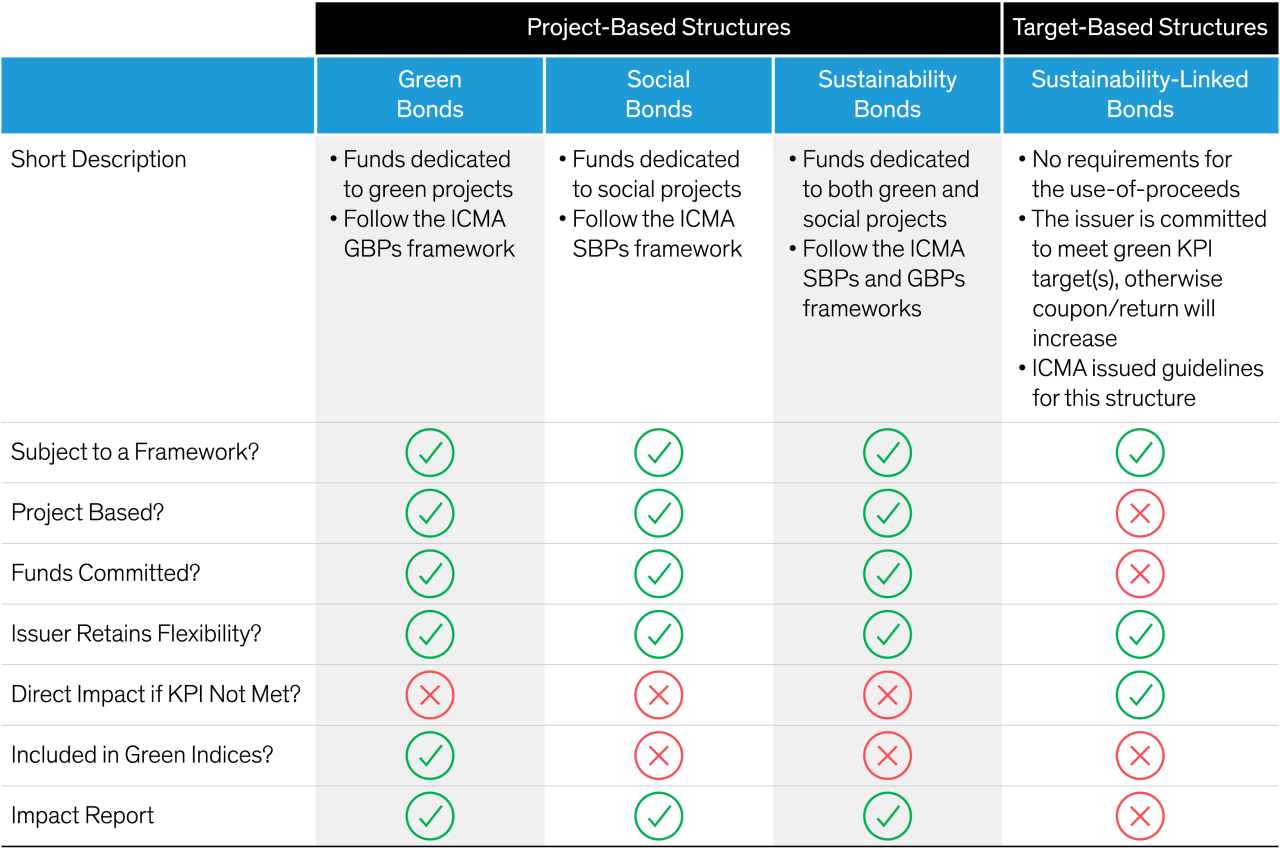
Many investors are already familiar with green bonds, which have been on the market since 2007. Green bonds finance a specific project or projects with an environmentally beneficial purpose. Since then, companies have issued new types of bonds to finance a range of green, social and sustainable projects (Display).
The most recent innovation—the sustainability-linked bond—is a target-based structure incorporating key performance indicators (KPIs). It incentivizes the issuing company to achieve higher ESG standards across the business, rather than to finance a specific project. Such initiatives give issuers considerable flexibility in raising capital on ESG-linked grounds.
The proliferation of ESG-linked bonds means investors need to be aware of the technical distinctions and the investment implications of each type.
Project-Based Structures
Despite the growing popularity of more recent structures, green bonds are still the biggest class of ESG-linked finance, with more than $1 trillion outstanding, according to the Climate Bonds Initiative. We like this structure because it supplies a clear link between capital investment and improving the environment, and it works well for many industries.
Even so, there are several intricacies that investors should bear in mind. Proceeds for each issue are meant to finance a green project (or range of projects) in line with a specified framework and timeline. But bondholders cannot force the issuer to use the proceeds for the stated projects or to deliver them on time. Effectively, investors in green bonds are relying on the reputation of the issuing company and must have confidence in its credentials.
Importantly, investors should be sure that the issuer’s projects are genuinely environmentally beneficial and not misrepresented, or “greenwashed.” That means verifying that the metrics established for a project’s impact report are specific, material and credible. For example, investors might determine whether a project that aims to reduce CO2 emissions will do so by a meaningful amount.
One development that helps frame certain types of impactful projects comes from Europe. The European Union (EU) has created a detailed taxonomy for sustainable activities that investors can refer to when authenticating green bond issues related to climate change mitigation and adaptation. Whenever possible, green bonds’ use of proceeds should align with the EU taxonomy. For euro-area companies—particularly high-yield issuers—that have been shy about issuing green bonds, this is welcome news, as the taxonomy allows them to identify green assets more easily.
We are closely watching similar developments in other regions, such as China. In the meantime, the leading index providers have established their own tests to determine whether bonds are genuinely green, though these can be subjective and aren’t exhaustive. As a result, inclusion in a green bond index doesn’t prove that a bond is truly green.
Social bonds work the same way as green bonds but finance socially impactful projects. Examples include new buildings for communal benefit, educational programs for an underprivileged demographic and more hospital beds for low-income areas.
We saw a resurgence in activity in this asset class in 2020, with issuers such as Italian national agency Cassa Depositi e Prestiti using this structure to help respond to the COVID-19 emergency and sustain the recovery of the Italian economy and communities.
Other project-based structures include sustainability bonds and sustainable development goal (SDG) bonds. Use of proceeds for sustainability bonds falls into both social and environmental categories, while for SDG bonds, the pool of eligible assets can be wider and align with one or more United Nations SDG.
Just as with green bonds, investors need to do due diligence on all project-based bond issuers and the credibility of their projects.
Target-Based Structures
The proceeds of sustainability-linked bonds (formerly called KPI-linked bonds) are meant for general corporate purposes, not for a specific project. 2021 saw a big uptick in this kind of issuance, as flexibility around use of proceeds opened the door for many high-yield and emerging-market issuers, some of which are in “dirty” industries and are transitioning to more climate-friendly processes.
Sustainability-linked bonds are based on a KPI at firm level. If the company fails to achieve the KPI within the specified timeline, it is penalized with a coupon step-up on the bond. Accordingly, investors must research the company’s overall sustainability strategy and determine whether the KPI aligns with that goal.
For sustainability-linked bonds, there is a direct and enforceable monetary incentive for the issuer to perform, rather than reputational risk only. This type of structure makes the issuing company accountable for executing on a top-down strategy that materially changes the sustainability of the business, as opposed to simply identifying and segregating a set of green assets while continuing with business as usual for its other activities.
That’s why we like certain sustainability-linked structures. We think, for instance, that greenhouse gas KPIs that are aligned with the 2 Degrees Investing Initiative are well suited for high-emitting sectors such as energy, cement and some chemicals manufacturers.
One possible reservation about sustainability-linked structures is that investors benefit from the coupon step-up if the issuer fails to hit its target. While some see this as a misalignment of incentives, we view it like step-ups that result from a credit downgrade—we don’t want the downgrade to happen but expect to be compensated if it does. In the future, sustainability-linked structures may be developed with different issuer incentives that further improve alignment with investors’ objectives.
That said, sustainability-linked structures need to be monitored for greenwashing, given the inherent flexibility around use of proceeds. KPIs must be chosen and calibrated carefully. And investors should actively engage with the issuer to get progress updates on achieving the KPI and to better understand the tools used to meet it.
Due Diligence Still Key in Evolving ESG-Labeled Bond Market
While investors now have a wide range of ESG-labeled bonds to select from, they need to conduct thorough due diligence—to analyze the specifics of each bond’s structure and to understand how it supports the overall sustainability strategy of the issuing company. Identifying the right choice will also depend on the investor’s particular investments and ESG approaches.
But investors can be confident that the market is continuing to evolve to supply more choices and better accountability.
The views expressed herein do not constitute research, investment advice or trade recommendations and do not necessarily represent the views of all AB portfolio-management teams. Views are subject to change over time.
View original content here

AllianceBernstein
AllianceBernstein
AllianceBernstein (AB) is a leading global investment management firm that offers diversified investment services to institutional investors, individuals, and private wealth clients in major world markets.
To be effective stewards of our clients’ assets, we strive to invest responsibly—assessing, engaging on and integrating material issues, including environmental, social and governance (ESG) considerations into most of our actively managed strategies (approximately 79% of AB’s actively managed assets under management as of December 31, 2024).
Our purpose—to pursue insight that unlocks opportunity—describes the ethos of our firm. Because we are an active investment manager, differentiated insights drive our ability to design innovative investment solutions and help our clients achieve their investment goals. We became a signatory to the Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI) in 2011. This began our journey to formalize our approach to identifying responsible ways to unlock opportunities for our clients through integrating material ESG factors throughout most of our actively managed equity and fixed-income client accounts, funds and strategies. Material ESG factors are important elements in forming insights and in presenting potential risks and opportunities that can affect the performance of the companies and issuers that we invest in and the portfolios that we build. AB also engages issuers when it believes the engagement is in the best financial interest of its clients.
Our values illustrate the behaviors and actions that create our strong culture and enable us to meet our clients' needs. Each value inspires us to be better:
- Invest in One Another: At AB, there’s no “one size fits all” and no mold to break. We celebrate idiosyncrasy and make sure everyone’s voice is heard. We seek and include talented people with diverse skills, abilities and backgrounds, who expand our thinking. A mosaic of perspectives makes us stronger, helping us to nurture enduring relationships and build actionable solutions.
- Strive for Distinctive Knowledge: Intellectual curiosity is in our DNA. We embrace challenging problems and ask tough questions. We don’t settle for easy answers when we seek to understand the world around us—and that’s what makes us better investors and partners to our colleagues and clients. We are independent thinkers who go where the research and data take us. And knowing more isn’t the end of the journey, it’s the start of a deeper conversation.
- Speak with Courage and Conviction: Collegial debate yields conviction, so we challenge one another to think differently. Working together enables us to see all sides of an issue. We stand firmly behind our ideas, and we recognize that the world is dynamic. To keep pace with an ever changing world and industry, we constantly reassess our views and share them with intellectual honesty. Above all, we strive to seek and speak truth to our colleagues, clients and others as a trusted voice of reason.
- Act with Integrity—Always: Although our firm is comprised of multiple businesses, disciplines and individuals, we’re united by our commitment to be strong stewards for our people and our clients. Our fiduciary duty and an ethical mind-set are fundamental to the decisions we make.
As of December 31, 2024, AB had $792B in assets under management, $555B of which were ESG-integrated. Additional information about AB may be found on our website, www.alliancebernstein.com.
Learn more about AB’s approach to responsibility here.
More from AllianceBernstein

